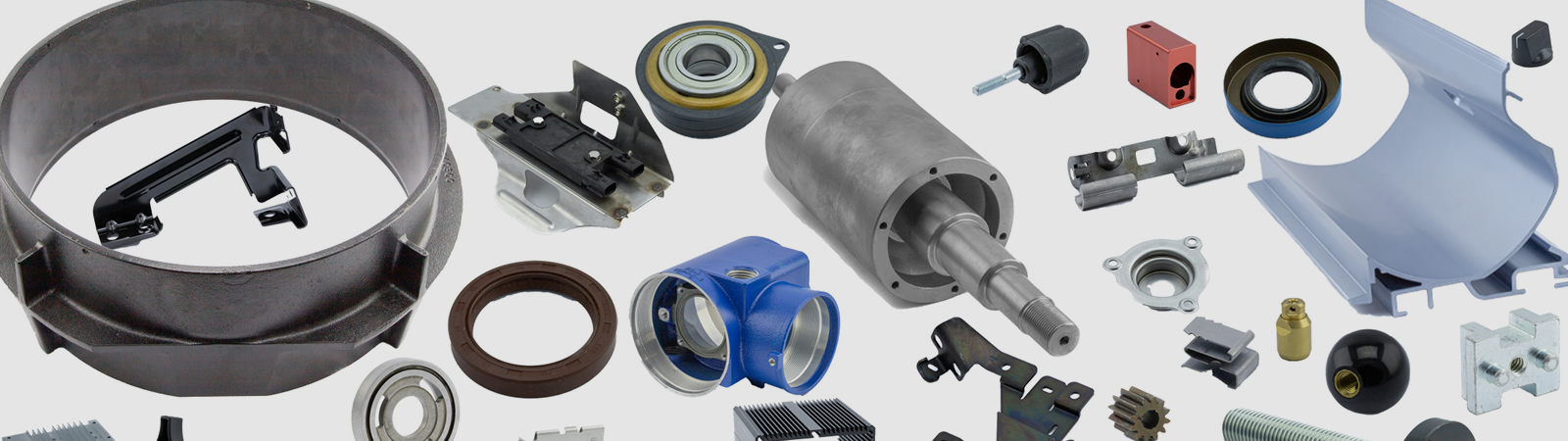
Gorham Incorporated represents world-class manufacturers that specialize in various manufacturing processes:
Aluminum Extrusions
Extruding is a manufacturing process of forcing aluminum billet through a shaped opening in a die, on an extrusion press. The extruded material emerges as an elongated piece with the same profile as the die opening. The basic principal of extrusion is as simple as squeezing toothpaste out of a tube. Pressure is applied at the closed end of the toothpaste tube, which forces the paste to flow through the open end. The shape, or profile, of the paste reflects the shape of the opening through which it is forced. Pressure in an extrusion press is applied by a hydraulic ram which forces heated aluminum billet through the container and out of the die. The amount of force dictates the size of the profile it is capable of producing; the higher the tonnage of the press, the larger the possible extrusion. The container of the extrusion press is a hollow chamber fitted with a removable liner. The container has a slightly larger inside diameter than the billet to be extruded. The die is a steel disc at the end of the container. Heated aluminum is forced through the opening in the die to create the extruded shape. Extrusion dies are available in three basic categories; solid, semi-hollow and hollow. Read more…
Metal Stampings
Stamping is a manufacturing process that utilizes coiled strip metal that passes through a series of progressive dies, punches and forms to produce a finished part. There are several different production metal stamping machines used in the industry. We specialize in progressive punch presses and multi-slide machines, both of which have distinct advantages and drawbacks. Punch press machines utilize virtually unlimited tonnage applied to the work for greater forming. Speed of these machines is also a benefit in some cases. Punch presses utilize a progression of dies in one unitized master tool. These tools are costed based on the intricacies of the finished part. The part progresses through the die into stations on a carrier strip and is cut off in the last station of the die. Multi-slide machines utilize coil strip or ribbon metal which passes through a punch press section that blanks out specific features. The part is then separated from the carrier strip and is sent into the forming or slide section of the machine. Form tools are located at right angles to each other, operating off cams in a horizontal or vertical plane and a center forming post. Each of these elements can be tooled to perform specific bending, forming, assembly, or part removal function. Multi-slide tooling tends to be less costly and more versatile than punch presses. Part configuration and quantity will determine what type of metal stamping machine is best to produce a finished part. Read more…
Precision Machining
Machining is a manufacturing process in which power-driven machine tools such as saws, lathes, milling machines and drill presses are used with a sharp cutting tool to mechanically cut the material to achieve the desired geometry. The traditional machining processes include turning, boring, drilling, milling, broaching, sawing, shaping, grinding, planning, reaming and tapping. Types of machines that produce precision machine components include screw machines (both single spindle and multiple spindle bar machines), CNC controlled horizontal and vertical machining centers and lathes. These machines utilize either metal bar stock, cast or forged metals. The quantity, accuracy, shape, finish and material will determine what type of machine should be used. Read more…
Machined Castings
The casting process is an essential manufacturing process to efficiently produce complex shapes. Casting is a process in which liquified material is poured into the cavity of a specially designed mold. The molten metal will solidify in the mold and then move onto the next process. Volumes and tolerances can dictate the casting process that is utilized. The various casting processes that we specialize in are sand castings, investment castings, permanent mold castings and die castings. Sand castings can be well suited for lower volume runs and fabricating large component parts. Investment castings have a higher degree of accuracy than sand castings, are better for thin walled parts with complex geometries and have a higher quality surface finish. Permanent mold casting is generally best suited for materials with lower melting temperatures such as zinc, copper, magnesium and aluminum alloys. Permanent mold castings can have tighter dimensional accuracy as well as excellent surface finish, and generally have a lower percentage of rejections. The high initial set up cost, however, can make permanent mold casting unsuitable for small production runs. Die casting is best for higher volume, tight size and shape tolerance component parts, and generally reduces the need for post machining. Read more…
Molding
Knobs & Handles – Manufactured through an injection molding process, knobs and handles are made from a thermoplastic or thermoset plastic material. Plastic pellet material is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and forced into a mold cavity where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the mold cavity. After a product is designed, metal molds are made by a moldmaker (or toolmaker) with either steel or aluminum, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection molding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of plastic parts, from the smallest knobs to entire auto body panels. Read more…
Seals – Seals are devices that prevent the passage of fluids along a rotating shaft. Seals are necessary when a shaft extends from a housing (enclosure) containing oil, such as a pump or a gearbox. Synthetic rubber, Viton and silicones are among the materials used for the sealing ring. We specialize in shaft seals, mechanical seals, bearing seals, hydraulic seals, v-ring seals, rubber gaskets, bearing isolations and custom molded rubber products. Our core competency is in custom seal design, application engineering, problem seal analysis and precision rubber manufacturing. Read more…
Fabrications, Powder Metal & More
Metal Fabrications – Metal fabrication is the creation of metal structures with cutting, bending and assembling processes. Typically large fabrication shops employ a multitude of value added processes, including welding, cutting, forming and machining. Read more…
Powder Metal – The powder metal (also called sintered metal) process consists of three basic steps; powder blending, die compaction and sintering. Dry powder is pressed into a mold that produces precise parts and then goes through a sintering process to create a stable part. This process is best suited for smaller complex parts that require tight tolerances. Read more…
Wire Rope & Lanyards – Wire rope is a type of rope which consists of several strands of metal wire laid (or ‘twisted’) into a helix. Initially wrought iron wires were used, but today steel is the main material used for wire ropes. Assemblies are quite common using wire rope and other components. Read more…
Springs & Wire Forms – A spring is an elastic object used to store mechanical energy and is generally made out of spring steel. We specialize in compression, torsion and extension springs that primarily service the automotive, valve and engine markets. Our spring diameter capabilities range from 0.003 to 0.090 wire. Our wire form diameter capabilities range from 0.007 to 0.170 wire. Read more…


 Commercial
Commercial